Heat conduction with phase change (manufactured solution)
Problem description
This benchmark is testing the extended version of a classical heat conduction equation which is capable of modeling ice formation and melting in water-saturated porous medium. It is sometimes termed ‘heat conduction equation with phase change’, or, with a slight abuse of notations, simply ‘T+freezing’ equation.
Since the equation is strongly non-linear in the temperature variable $T$, a carefully designed code verification is a must and is performed. To this end, we use the concept of a manufactured solution, when a prescribed function (in this case, it is $T$) is plugged in the corresponding boundary-value problem yielding the heat source-term, as well as it also provides the initial and boundary conditions. This recovered/extracted data-set is then used in the OGS code as the corresponding input, and the obtained numerical solution can be compared with the prescribed (manufactured) counterpart.
See this PDF for the detailed description.
Test case
In the benchmark test, we restrict ourselves to the problem formulated in the unit square and on the unit time-interval. The manufactured solution is constructed in such a way that its evolution in time mimics the simultaneous ice melting-forming process in the domain, as in the following figure:
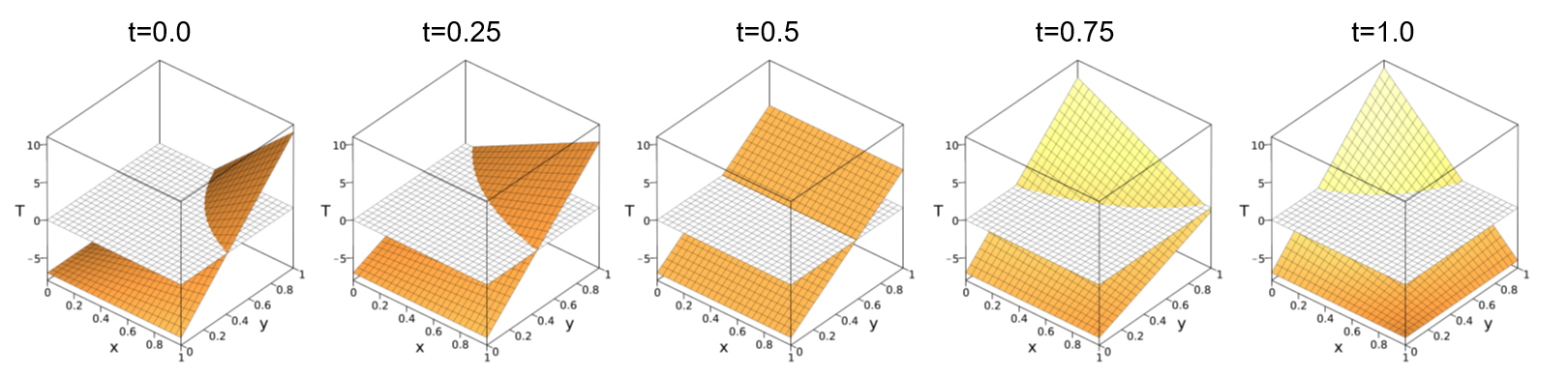
The plane in white color in figure represents zero (melting) temperature in Celsius, such that the zero-level set of $T$ mimics the interface between ice and water fractions which moves in time.
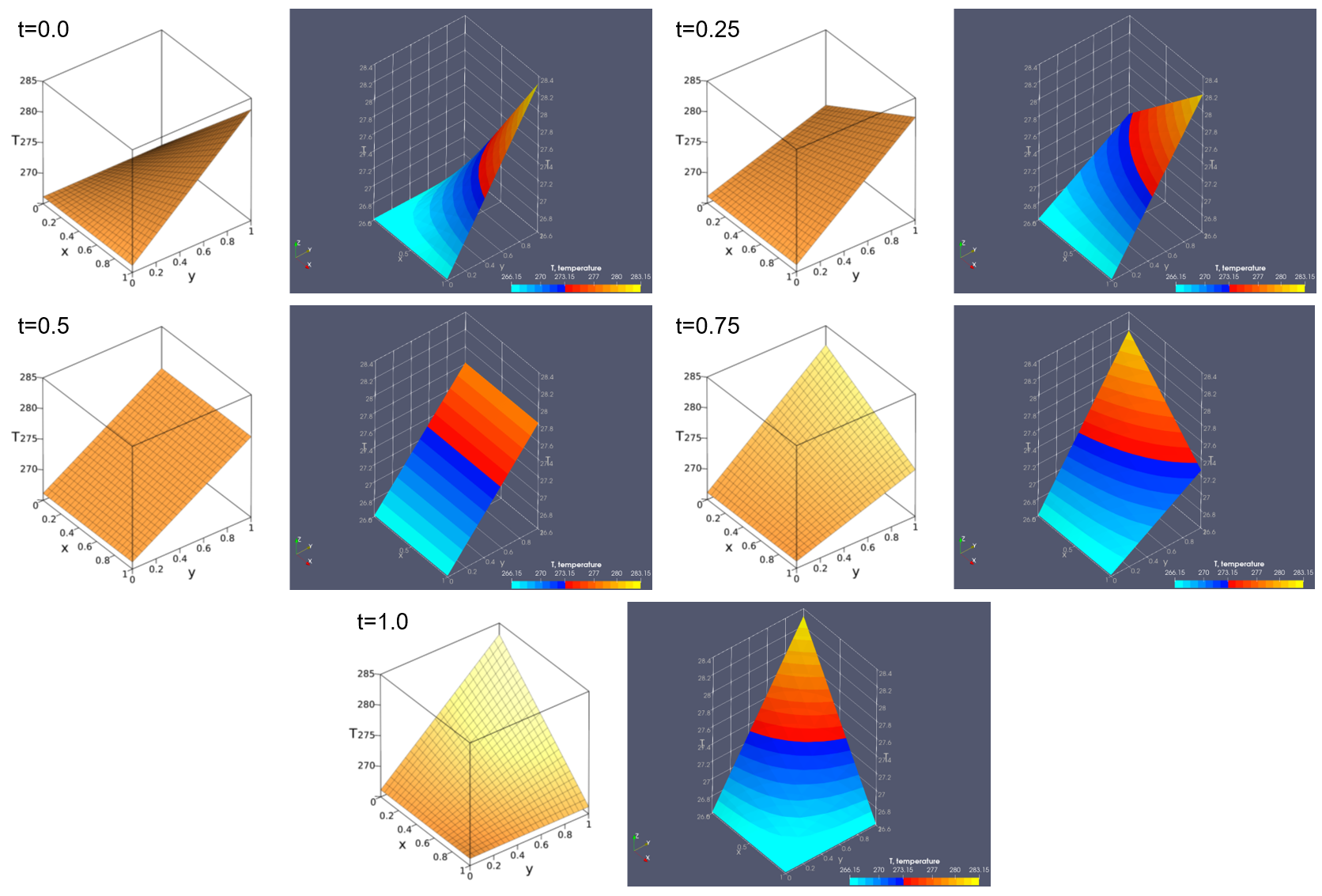
Next figure depicts comparison of the manufactured solution and the numerical one at different time steps. The temperature given in Kelvins. Note that we have made the vertical range of the OGS solutions in the ParaView plots $10^{-1}$ rescaled, to make the comparison feasible. Also, we have tuned the color legend in the ParaView plots such that the ice and water fractions can be visible/identified.
The test is presented in:
Parabolic/T/2D_Ice_melting-forming_manuf_solution/ManSol3_IceWaterMix_Scaled.prj ,
This article was written by Tymofiy Gerasimov. If you are missing something or you find an error please let us know.
Generated with Hugo 0.122.0
in CI job 449919
|
Last revision: April 23, 2024
Commit: [PL/LD] Use generic cell average output 3557e29
| Edit this page on