Introduction
Installation
There are various ways to obtain a (pre-built) running version of OpenGeoSys (OGS) on your machine. You can have OGS for different operating systems including Windows, Linux, and macOS. The basic modelling platform is available for all operating systems. The different operating systems and installation methods give you the feature matrix:
| Operating system / Installation method | Processes | MFront | PETSc |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows / pip & binary download | TH2M disabled, see issue |
❌ | ❌ |
| macOS / pip | All | ✅ | ❌ |
| Linux / pip & Serial Container | All | ✅ | ❌ |
| Linux / PETSc Container | All | ✅ | ✅ |
Using Linux binaries on other operating systems
Please note that you can use Linux binaries installed via pip or in the form of a container also on other operating systems.
For Windows we recommend the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL).
On macOS you can use either a virtual machine (e.g. via UTM) or run a Docker container.
Install via pip
A straightforward way of installing OGS is via Python’s pip-tool:
# Optional: create a Python virtual environment, see below
python -m venv .venv
.\venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1
# Install latest ogs release (6.5.5) via pip:
pip install ogs
# OR: Install latest ogs master (weekly) via pip:
pip install --pre --index-url https://gitlab.opengeosys.org/api/v4/projects/120/packages/pypi/simple ogsIf you get errors when calling the Activate.ps1 script you have to run the following command once:
Set-Execution-Policy Unrestricted -Scope CurrentUser# Optional: create a Python virtual environment, see below
python -m venv .venv # or `python3 -m venv .venv`
source .venv/bin/activate
# Install latest ogs release (6.5.5) via pip:
pip install ogs
# OR: Install latest ogs master (weekly) via pip:
pip install --pre --index-url https://gitlab.opengeosys.org/api/v4/projects/120/packages/pypi/simple ogsPlease note that this requires a Python installation (version 3.8 - 3.11) with the pip-tool.
We recommend using Python within a virtual environment to keep possible
conflicts of different Python-packages localised. If you use pip for installation of OGS in a virtual environment and you
activate the virtual environment, then OGS and its tools are automatically also in the PATH. If the virtual environment is
not activated you may still use OGS, but either have to give the full path to ogs being located in the bin folder (or Scripts folder on Windows) of the
virtual environment, or add this path to your PATH-environment. Moreover, pip may print instructions which directory needs
to be added to the PATH.
Advanced usage: Use binaries from PATH instead of pip package
When using the OGS Python bindings it may be desired to use a different OGS version than provided by the pip package. This can be achieved by setting the environment variable OGS_USE_PATH. E.g.:
pip install ogs
# now ogs from pip is used
export PATH=/path/to/ogs/bin:$PATH
OGS_USE_PATH=1 python
# now in Python interpreter:
>>> import ogs
>>> ogs.cli.ogs("--version") # uses /path/to/ogs/bin/ogs instead of ogs from pipAlternative: Install via binary downloads
Another way to obtain a running version is to just download the latest stable or development release of OpenGeoSys from the Releases-page.
By downloading from the release page you will get a bunch of folders and files. However, OGS itself will come as a simple
executable file, which you will find in the bin sub-folder. You can put the executable wherever you like. For convenience you
may put it into a location which is in your PATH-environment variable or modify the PATH environment variable which allows you to start the executable without
specifying its full file path. Then just calling ogs from the terminal is sufficient.
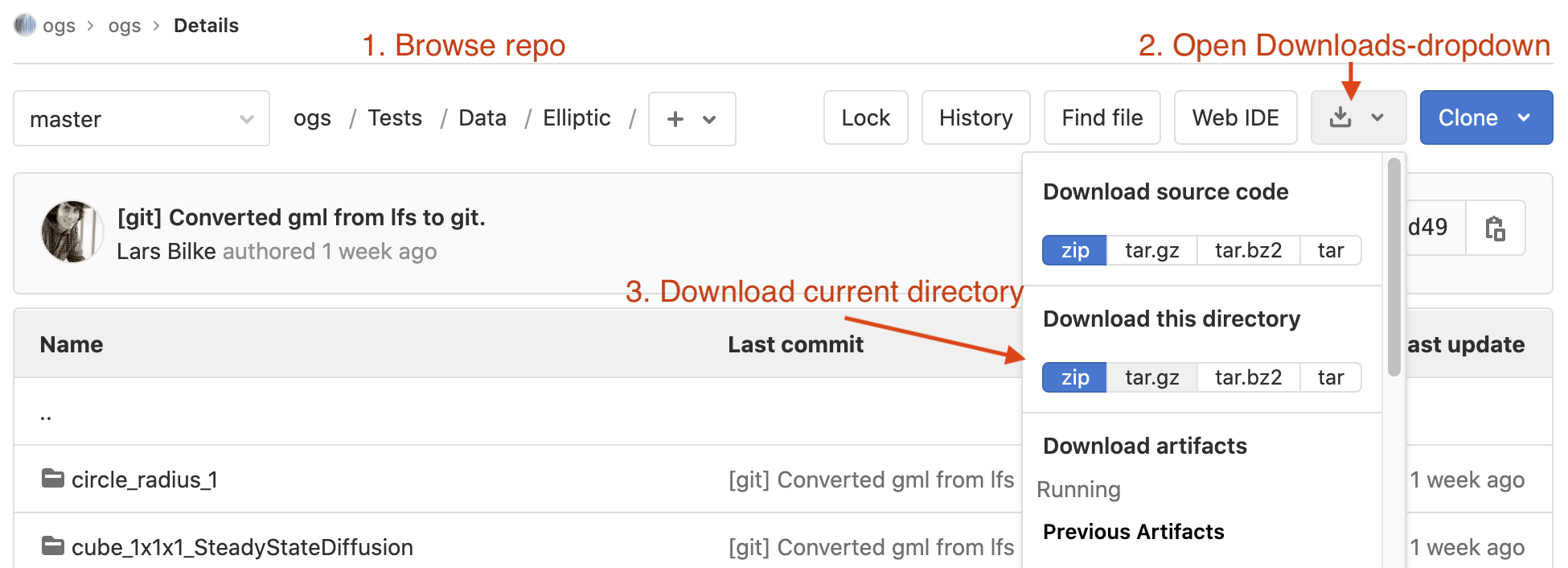
Download benchmarks
You can download the latest benchmark files from GitLab:
- On our OGS repository on GitLab browse to the Tests/Data -folder
- Browse to the process subfolder you are interested in, e.g. Elliptic (1.)
- Find the Downloads-dropdown (2.)
- Choose an appropriate format under Download this directory (3.)
- Uncompress the downloaded file
See the Benchmarks section for more information on the benchmarks.
Running
OGS is a command line application and requires the path to a .prj-file as an argument.
To run it open a new command line shell (called cmd.exe). Now simply type ogs (if the executable is in your PATH
-environment variable) or specify its full path (e.g.: C:\Users\MyUserName\Downloads\ogs.exe) and hit ENTER.
OGS prints out its usage instructions:
PARSE ERROR:
Required argument missing: project-file
Brief USAGE:
ogs [--] [--version] [-h] <PROJECT FILE>
For complete USAGE and HELP type:
ogs --helpYou can see that there is the project-file missing.
Then simply supply the path to a project file as an argument to the OGS executable:
ogs .\Path\to\BenchmarkName.prjTo run it open a new command line shell (Terminal). Now simply type ogs (if the executable is in your PATH-environment
variable) or specify its full path (e.g.: ./path/to/ogs) and hit ENTER.
OGS prints out its usage instructions:
PARSE ERROR:
Required argument missing: project-file
Brief USAGE:
ogs [--] [--version] [-h] <PROJECT FILE>
For complete USAGE and HELP type:
ogs --helpYou can see that there is the project-file missing.
Then simply supply the path to a project file as an argument to the OGS executable:
ogs ./path/to/BenchmarkName.prjTo run it open a new command line shell (Terminal). Now simply type ogs (if the executable is in your PATH-environment
variable) or specify its full path (e.g.: ./path/to/ogs) and hit ENTER.
OGS prints out its usage instructions:
PARSE ERROR:
Required argument missing: project-file
Brief USAGE:
ogs [--] [--version] [-h] <PROJECT FILE>
For complete USAGE and HELP type:
ogs --helpYou can see that there is the project-file missing.
Then simply supply the path to a project file as an argument to the OGS executable:
ogs ./path/to/BenchmarkName.prjThis article was written by Lars Bilke. If you are missing something or you find an error please let us know.
Generated with Hugo 0.147.9
in CI job 577984
|
Last revision: July 2, 2025
Commit: [ci,web] Replace pipx run with uvx. 0e82df3b
| Edit this page on