GitLab CI
Introduction
GitLab CI is a powerful Continuous Integration system integrated into GitLab.
The tasks of the CI system are configured in scripts inside the OGS source code. The entry point is defined in .gitlab-ci.yml. Scripting and versioning the configuration together with the source code is very powerful, e.g. if you introduce a new OGS CMake configuration in a merge request even the change of the CI jobs configuration or jobs environment (Docker container definition) can be part of the merge request.
GitLab Pipeline
A CI run consists of a pipeline which contains stages which in turn contain jobs. A job runs a set of instructions (e.g. checking out the source code, building the code, testing the code) on a runner.
Each pipeline run is visualized as follows:
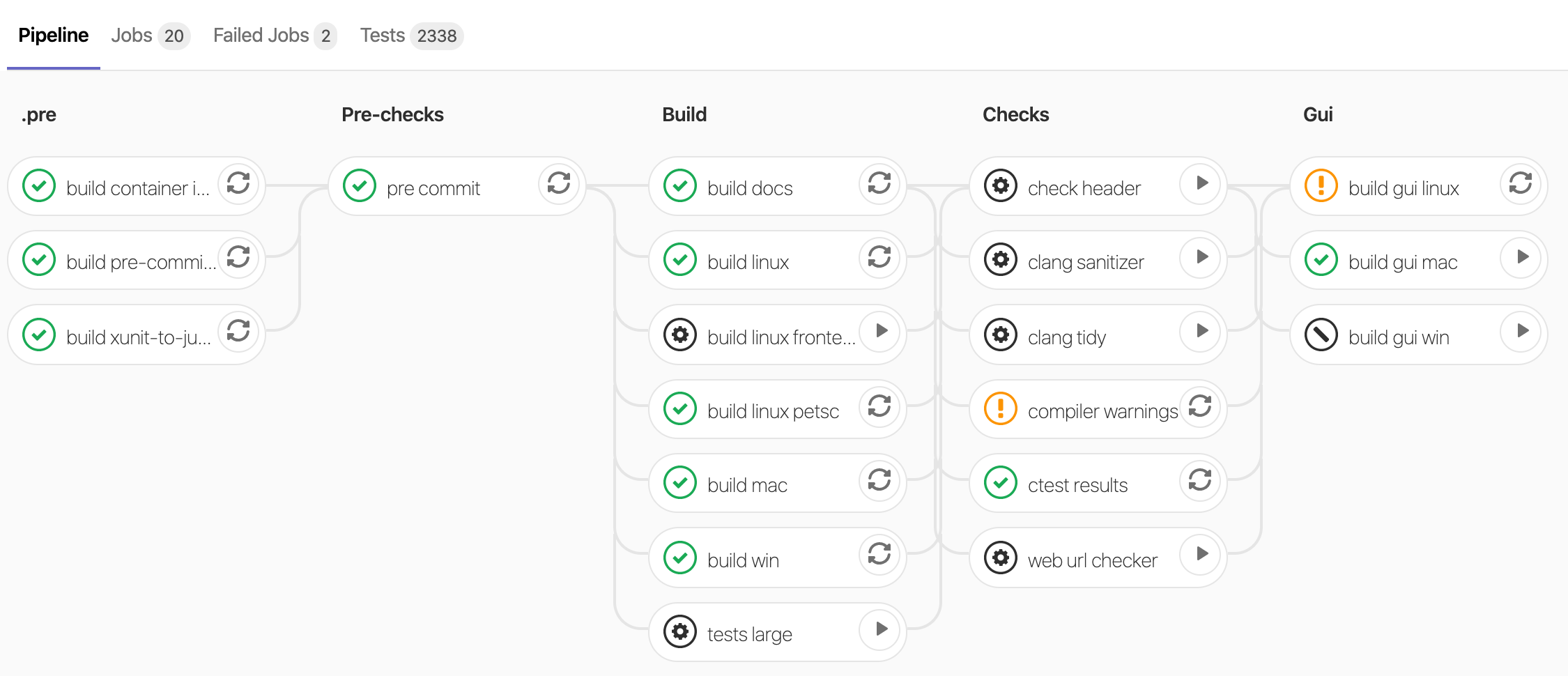
Jobs belong to a stage and each job will get a status (success, warnings, failure). Some jobs are optional (see the gear icon) and can be manually triggered by pressing the play button.
Automatic testing
The master-branch of the main repository as well as all merge requests on that repository are automatically tested. See the pipelines page.
Skip automatic testing
If you want to skip a pipeline run for a push add the -o ci.skip git push option. Example:
git push -o ci.skipOr add [ci skip] to the commit message to skip the pipeline for this commit. Example:
git commit -m "Added feature X [ci skip]"Or use the merge request label ci::skip.
(Temporarily) reduce pipeline run time
During work on MR you may want to reduce the pipeline run time to get feedback faster. You can use a pre-configured reduced pipeline or manually editing the pipeline configuration files.
Pre-configured reduced pipelines
These pipelines can be selected by using merge request labels:
ci::web only: Runs Jupyter notebook ctests only and builds the web site.ci::linux onlyandci::mac onlyandci::win only: Runs platform specific builds only.
More MR labels affecting CI pipelines
ci_largefor enabling large ctests in merge request pipelines. Combine withci::linux onlyfor faster feedback on the benchmarks.
Manually editing .gitlab-ci.yml and scripts/ci/pipelines/regular.yml
You can change the pipeline by editing the .gitlab-ci.yml and scripts/ci/jobs/*.yml files. It is good practice to mark these changes with commits starting with drop: ... in the commit message so they can be removed later easily.
These variables in .gitlab-ci.yml modify the pipeline:
BUILD_TESTS: Set this tofalseto disable unit tests.BUILD_CTEST: Set this tofalseto disable CTest (benchmark) tests.CTEST_ARGS: Supply additional arguments to thectest-command to select which benchmarks are run, e.g.:-R nbwould select all notebook-based tests and would disable all other benchmarks-LE largewould exclude all tests with labellarge
All jobs get included in the include:-section in the file scripts/ci/pipelines/regular.yml. You can simple comment out files to disable jobs defined in that files. Please note that some jobs depend on other jobs.
scripts/ci/jobs/*.yml
All jobs are defined in these files. You can disable a single job by prefixing its name with a dot, e.g.:
# enabled job:
build linux arch:
# disabled job:
.build linux arch:This article was written by Lars Bilke. If you are missing something or you find an error please let us know.
Generated with Hugo 0.122.0
in CI job 449919
|
Last revision: April 23, 2024
Commit: [PL/LD] Use generic cell average output 3557e29
| Edit this page on