ExtractMaterials
Description
This tool takes a mesh with multiple material IDs and writes elements of a specific ID to a new mesh. If no ID is specified, meshes are created for each existing material ID.
Usage
USAGE:
ExtractMaterials -i <input file name> -o <output file name>
[-m <Number specifying the MaterialID>]
[--] [--version] [-h]
Where:
-i <input file name>, --input <input file name>
(required) Name of the input mesh (*.vtu)
-o <output file name>, --output <output file name>
(required) Name of the output mesh (*.vtu)
-m <Number specifying the MaterialID>, --material-id <Number specifying
the MaterialID>
The MaterialID for which elements should be extracted into a new mesh.
--, --ignore_rest
Ignores the rest of the labeled arguments following this flag.
--version
Displays version information and exits.
-h, --help
Displays usage information and exits.Example:
In this example we use a 3D mesh (Fig.1) and extract its elements of material ID 3 to create a new mesh.
ExtractMaterials -i mesh_layered.vtu -o mesh_exMatId.vtu -m 3
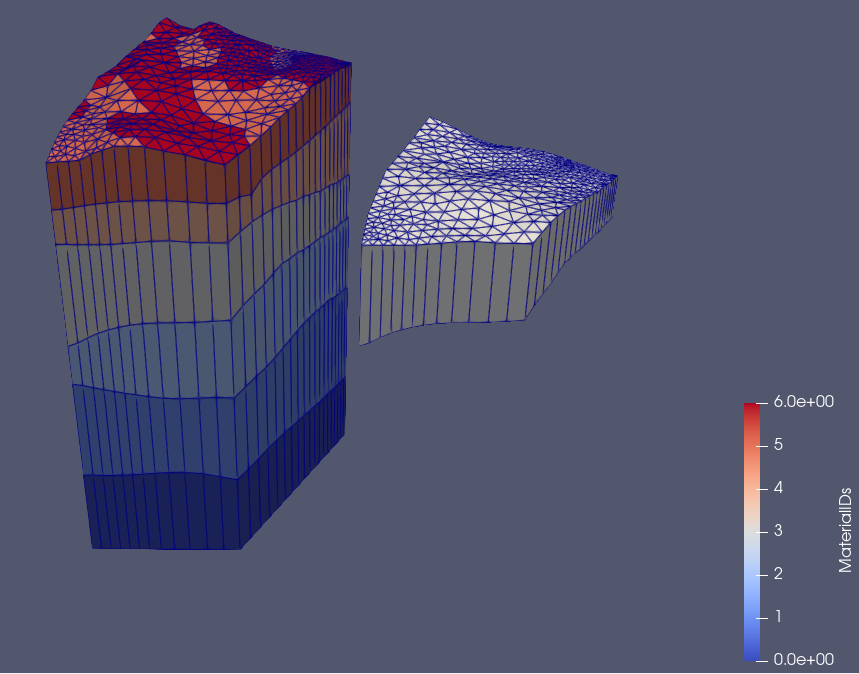
Fig.1 The left side shows a layered 3D input mesh created from raster files using the tool createLayeredMeshFromRasters. The different colors depict different material IDs. The z-values of the meshes are scaled by a factor of 10. The right mesh shows the extracted mesh. In this graphic it is translated along the x-axis, its spatial coordinates are not altered by the ExtractMaterials-tool.
This article was written by Julian Heinze. If you are missing something or you find an error please let us know.
Generated with Hugo 0.122.0
in CI job 570044
|
Last revision: April 17, 2025
Commit: Rewrite using ranges 1ed34f4
| Edit this page on